In today’s fast-paced business environment, staying ahead of the competition requires leveraging cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions. One such solution that has gained significant traction in recent times is Large Language Models (LLMs). LLMs have the potential to transform the way organizations operate, and their impact is being felt across industries. This article will provide an in-depth overview of LLMs, their features, capabilities, and applications. We will also explore the benefits and limitations of LLMs and discuss the future outlook of this technology.
Features and Capabilities of LLMs
LLMs are a class of artificial intelligence models that are specifically designed to process and generate human-like language. These models are trained on massive datasets of text, which enables them to learn patterns and relationships within languages. The following are some of the key features and capabilities of LLMs:
-
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): LLMs are equipped with NLU capabilities that allow them to comprehend and interpret human language. This feature enables LLMs to extract meaning and context from text data, which is essential for applications such as sentiment analysis, question-answering, and summarization.
-
Natural Language Generation (NLG): LLMs can generate human-like text, which is often indistinguishable from text written by humans. This capability has numerous applications, including content creation, language translation, and chatbots.
-
Contextual Understanding: LLMs can understand context, which is critical for applications that require nuanced and personalized responses. For instance, a chatbot powered by an LLM can understand the context of a conversation and respond accordingly.
-
Adaptive Learning: LLMs are designed to learn from feedback, which enables them to improve their performance over time. This adaptive learning capability ensures that LLMs remain accurate and relevant even as language evolves.
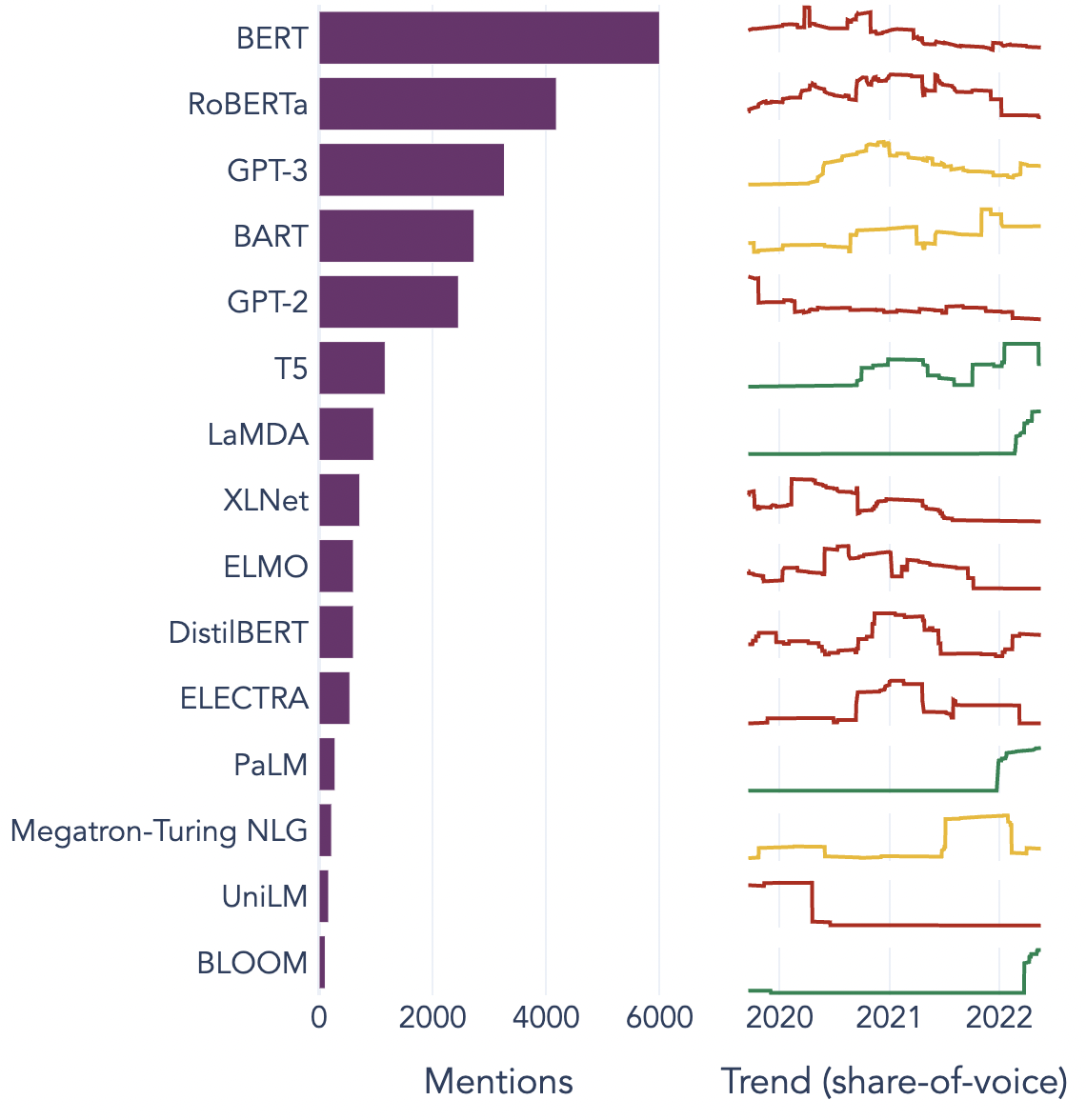
Most popular LLM’s
Applications of LLMs
The versatility of LLMs makes them applicable to a wide range of industries and use cases. Some of the most common applications of LLMs include:
-
Chatbots: LLMs can be used to create intelligent chatbots that can engage with customers, answer queries, and resolve issues. Chatbots powered by LLMs offer several advantages, including reduced response times, improved accuracy, and enhanced customer experience.
-
Content Creation: LLMs can generate high-quality content quickly and efficiently. This capability has numerous applications, including content marketing, social media management, and journalism.
-
Language Translation: LLMs can translate text from one language to another, which has numerous applications in fields such as diplomacy, tourism, and e-commerce.
-
Sentiment Analysis: LLMs can analyze text data to determine sentiment, which is crucial for businesses looking to gauge customer opinion and sentiment.
-
Question Answering: LLMs can answer questions based on the information they have been trained on, which has numerous applications in areas such as customer support and tutoring.
Benefits of LLMs
The benefits of LLMs are numerous, and they include:
-
Time Efficiency: LLMs can process and generate text at incredible speeds, reducing the time required for manual processing and creation. This efficiency can lead to cost savings and increased productivity.
-
Improved Accuracy: LLMs can accurately analyze and generate language, minimizing errors and improving overall quality. This accuracy is critical for applications where precision is paramount.
-
Enhanced Personalization: LLMs can be tailored to individual preferences, enabling personalized interactions and communications. Personalization can lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Cost Savings: LLMs can reduce costs associated with manual labor, improving profitability and efficiency.
Limitations of LLMs
While LLMs offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations. Some of the key limitations include:
-
Training Data: LLMs are only as good as the data they are trained on. Biases in training data can result in biases in the output generated by LLMs.
-
Ethical Concerns: LLMs raise ethical concerns related to privacy, bias, and job displacement. Organizations must address these concerns when implementing LLMs.
-
Limited Domain Knowledge: LLMs are domain-specific, which means they may not be effective outside their area of expertise.
-
Vulnerability to Attacks: LLMs can be vulnerable to attacks such as phishing and spoofing, which can compromise their integrity.
Future Outlook of LLMs
The future outlook of LLMs is promising, with numerous opportunities for growth and expansion. Some of the trends that are expected to shape the future of LLMs include:
-
Multimodal Language Processing: Future LLMs will be able to process and generate multimodal data, including images, videos, and audio.
-
Explainability and Interpretability: There will be an increasing focus on developing LLMs that can provide clear explanations and interpretations of their decision-making processes.
-
Edge AI: With the proliferation of edge devices, LLMs will be deployed on edge devices, enabling faster processing and reduced latency.
-
Human-AI Collaboration: Future LLMs will be designed to collaborate with humans, enabling hybrid intelligence systems that leverage the strengths of both humans and machines.
Conclusion
Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to transform the way organizations operate, and their impact is being felt across industries. From chatbots and content creation to language translation and sentiment analysis, LLMs offer numerous applications that can improve efficiency, accuracy, and personalization. However, LLMs also have limitations, including biases, ethical concerns, limited domain knowledge, and vulnerability to attacks. Despite these limitations, the future outlook of LLMs is promising, with numerous opportunities for growth and expansion. As AI continues to evolve, LLMs will play an increasingly important role in shaping our future.